Author: Prof.Dr. Darko Trifunović, Institute for National and International Security, Belgrade, Serbia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37458/nstf.26.1.7
Review paper
Received: April 21, 2025
Accepted: May 2, 2025
Abstract: Technical progress and technological development have enabled us to adopt innovative approaches in the fight against terrorism. Intelligence services plays a unique role in this fight. Their main task is to collect and analyze data and information on terrorist organizations, groups, and individuals. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and other new working methods are increasingly being used in the work of intelligence services. The bearers of terrorist threats posed by terrorist
 perpetrators or malicious actors in modern circumstances use everything at their disposal, especially in the form of cyberterrorism. Likewise, the Russian full scale aggression on Ukraine on 2022 has employed the massive use of drones. An identical situation exists simultaneously in the Middle East, where state sponsors of terrorism, namely Iran, are also using drones on a massive scale, primarily through proxy networks in Lebanon, Gaza, and Yemen. Russia uses its proxies via Iran to the Houthis in Yemen to attack cargo ships and thereby terrorize international shipping traffic. It logically follows that terrorists will increasingly use drones of diverse types along with AI in the future to support their operations. Intelligence services must improve in all ways to promptly detect such threats. We can speak about the New Craft of Intelligence in modern circumstances, given that the entire data collection, processing, analysis, and prediction cycle depends on understanding and adapting intelligence services to these new challenges and sophisticated technologies.
perpetrators or malicious actors in modern circumstances use everything at their disposal, especially in the form of cyberterrorism. Likewise, the Russian full scale aggression on Ukraine on 2022 has employed the massive use of drones. An identical situation exists simultaneously in the Middle East, where state sponsors of terrorism, namely Iran, are also using drones on a massive scale, primarily through proxy networks in Lebanon, Gaza, and Yemen. Russia uses its proxies via Iran to the Houthis in Yemen to attack cargo ships and thereby terrorize international shipping traffic. It logically follows that terrorists will increasingly use drones of diverse types along with AI in the future to support their operations. Intelligence services must improve in all ways to promptly detect such threats. We can speak about the New Craft of Intelligence in modern circumstances, given that the entire data collection, processing, analysis, and prediction cycle depends on understanding and adapting intelligence services to these new challenges and sophisticated technologies.
Keywords: Intelligence, Artificial Intelligence, Terrorism, Counter-terrorism, radicalization, de-radicalization.
Introduction
Terrorism is one of the most critical security threats facing modern society. This paper will define this phenomenon and establish how and in what way the state as an organized society confronts these and similar threats. Since one of the single largest terrorist attacks in modern history, which occurred on September 11, 2001, the terrorist threat has not been suppressed despite the Global War on Terrorism. On the contrary, the number of terrorist attacks is increasing. Do states have an institutional response to the imminent terrorist threat? Do our institutions see and analyze this threat? The answers should be sought in the intelligence services and how a security system is established and functions in a particular state. For a state security system to be established, function, and develop, that system must employ quality personnel with clear vision and responsible leadership. Of course, there are also issues with sophisticated equipment and working conditions, but the most crucial link is the "human factor" or the collection and analytical capabilities employed in Intelligence.
To understand the security system, it is essential to comprehend security science first. In this complex sphere, if the security phenomenon or threat itself is not understood, it isn't easy to apply specific responses from the technical and technological side. Understanding security phenomena or threats requires a broader education process in the security science field. This science is the basis for a country's security system. Security Culture is the main goal sought to be achieved (Piwowarski, J., Trifunovic, D. 2023). A justified question, therefore, arises: do all countries have a well-developed intelligence community? This refers not to a robust but to an efficient system that can protect society and the country from internal and external security threats.
Terrorism
To better understand the relationship between Intelligence and counterterrorism, it is paramount to properly define the terms and determine the bridge between these two terms. Although many theorists claim that there is no commonly accepted definition of terrorism, in practice, it looks completely different. Namely, almost every country has integrated this criminal offense into its legislation. What exactly is terrorism? By analyzing the content of the majority of existing definitions of terrorism, it can be concluded that the following elements are common: threat, violence, force; fear; political aspect - effect - goal; psychological effect and uncontrolled reaction; indiscriminate selection of targets and victims; deliberately planned and systematically organized action; method of combat; and unlawful act. From the above key elements of terrorism, it can be concluded that terrorism is an illegal act of violence directed against a particular state to cause fear or collective harm to achieve a specific political goal. It is about the intended use of force, and terrorism is used as a method of combat to achieve the aforementioned political goals (Trifunovic, D. 2021).
For any terrorist act to be carried out, two key elements must be met:
1. Operational capability to carry out the attack. This includes the availability of weapons, explosives, or other means of execution, such as knives and vehicles, which terrorists have often used. For terrorists, the goal they want to achieve is essential. In this context, they have a wide range of means to carry out their intentions. These operational possibilities must be the subject of interest for intelligence services, and they must pay great attention to both the profiles of terrorist organizations and their ambitions to carry out an attack. In this context, special attention must be paid to all possible means of mass destruction, such as chemical, biological, nuclear-atomic, and radiological agents. In modern times, it is easy to come across substances that are not dangerous on their own, but, in combination with others, can cause a dangerous reaction, such as binary poisons. Terrorists, and also state entities that implement the same methods as terrorists, as is the case with the proxies of the Houthis, who are increasingly using cutting-edge means such as drones (unmanned aerial vehicles) or AI or hypersonic missiles to attack civilian targets in the Red Sea (Aljazeera, 2024).
Many authors have pointed out the role and importance of unmanned aerial vehicles as possible means of carrying out terrorist attacks. Unmanned aerial vehicles are one of the three forms of unmanned systems that, in addition to air travel, can be designed for autonomous and/or controlled movement under or on the water surface and on land (Akrap, G. and Kalinić, P. 2018). It is to be expected, and the role of intelligence services is crucial, that terrorists will increasingly use sophisticated means such as drones of various types, as well as AI-guided means. Terrorist organizations such as Hamas and Hezbollah already use drones in their attacks. The terrorist organization DAESH poses a significant threat. "Innovative terrorism can be described as the introduction of a new method or the development of an existing technology by terror organizations. Considering the changing traits of terrorism and the resources owned by terror organizations today, its character and patterns of using innovative terrorism make DAESH the most dangerous organization threatening regional and international stability (Balkan, S., 2017).
2. Motive or motivation to carry out the terrorist attack. Intelligence services, in their analytics and their special departments, must deal with the key element for carrying out every terrorist attack. This is the motive or motivation that comes from various sources. Mostly, religion or the abuse of religion, the ideologies of various ultra-radical organizations, whether they are ultra-leftist or ultra-rightist, are important here. These considerations are essential not only for the detection of terrorists and the discovery of the source of motivation but also for the de-radicalization process. If intelligence services discover that there are processes of radicalizing specific structures on the state's territory, it is their obligation to do everything to prevent it.
Security science
In order to properly understand and analyze security phenomena, security risk factors, and security threats, both internal and external, it is necessary to know what security science is.
Several relevant international security experts, professors and scientists, offered a definition of Security Science to the professional and scientific community. The word "security" itself: Whether it is the Serbian word bezbednost, the Latin securitas, the English security, the ancient Greek asphalea, or the Hebrew word bitachon, the meaning is the same. It describes the condition/s of the state as an organized society. And not just any condition/s, but a condition without danger, without decay, non-existence of fears, etc. Security as a science means the condition of a state as an organized society. It is not just any condition, but a condition affected by external and internal risk and threat factors. This condition of the state must enable the smooth functioning of the state and its development. The science of security is based on several significant theories. These are the Theory of State, Theory of Law, Theory of Conflict, Theory of Multi-Complex Systems, Theory of Gambling, and Theory of Disaster. The science of security uses all the methods of social sciences and humanities as general methods; however, what separates it from others and makes it a science are its unique methods that do not come from the social sciences but rather from the natural sciences. These are data collection, processing, analysis, and prediction methods. (Todorovic, B.,& Trifunovic, D. 2020), (Kazansky, R., & Trifunovic, D. 2021)
Intelligence and Intelligence Gathering in Counter Terrorism
Intelligence is part of the national security system. Law or laws of the state define the role and place of the Intelligence Service. The same applies to the jurisdiction of the Intelligence Service. The main challenges facing any intelligence service arise when it comes to criminal acts, such as terrorism. In the analysis of the terrorist threat, the main task and approach is to discover or detect the key elements (indicators) of the terrorist threat:
1. Definition of the presence of terrorist organizations, groups, or subgroups. US under Section 219 of the Immigration and Nationality Act (INA) define terrorist organization: “A Foreign Terrorist Organization (FTO) is a foreign organization that engages in terrorist activity or retains the capability and intent to engage in terrorism, and whose terrorist activity threatens the security of U.S. nationals or U.S. national security." The EU defines terrorist groups within its Council Common Position 2001/931/CFSP: "A terrorist group means a structured group of more than two persons, established over a period of time and acting in concert to commit terrorist acts. “Groups committing intentional acts that seriously destabilize or destroy fundamental political, constitutional, economic, or social structures of a country .
2. Presence of terrorists. It very often happens that in a particular territory, there are fragments or from place to place terrorists who found themselves there due to various circumstances. A more serious situation arises when terrorist organizations, groups, or subgroups appear on the territory.
3. Presence of a state or states "sponsoring terrorism." A state sponsor of terrorism is a state whose government supports various organizations, groups, subgroups, or individuals that use terrorism as a method. This support is reflected in military, security, intelligence, logistical, and any other assistance, including diplomatic activities.
4. Presence of so-called non-governmental organizations designated to provide logistics to the bearers of the terrorist threat. International bodies, like the UN, EU, and FATF (Financial Action Task Force), monitor and sanction such entities.
5. Detection of carriers of motivations and triggers of terrorism: from religion to various ideologies. Such organizations are actually fronts and were established with the intention of hiding the identity of the sponsors, abusing humanitarian work, and providing logistics to terrorist organizations.
There may be, and indeed are, more elements of the terrorist threat, but these five are the most characteristic of operational fieldwork. These five elements are particularly evident when it comes to the terrorist threat of Islamists or jihadists. If using special security science methods that involve the application of a complete intelligence cycle with verification of data and information, the presence of all five elements or a more significant part is determined, we can conclude with high probability that a terrorist infrastructure is being or has been developed on the territory of a given country to carry out attacks in that country or use the territory of that country for operations against another. For example, for years, the intelligence services of some Western countries, especially in Europe, have neglected the presence of the five elements listed on their territory, as is the case in Austria, Germany, and France. Neglecting to detect the elements of a terrorist threat and act to suppress them has the goal of causing suffering to citizens and loss of life. According to the Global Terrorism Database, University of Maryland, "The vast majority of terrorist attacks in Europe deliberately target civilians, public spaces, and non-combatants to maximize psychological impact ." Despite significant advancements in intelligence capabilities, there are several reasons why intelligence services sometimes fail to prevent terrorist attacks, leaving civilians as the ultimate victims. Counterterrorism is a highly complex task, and intelligence gathering is not foolproof.
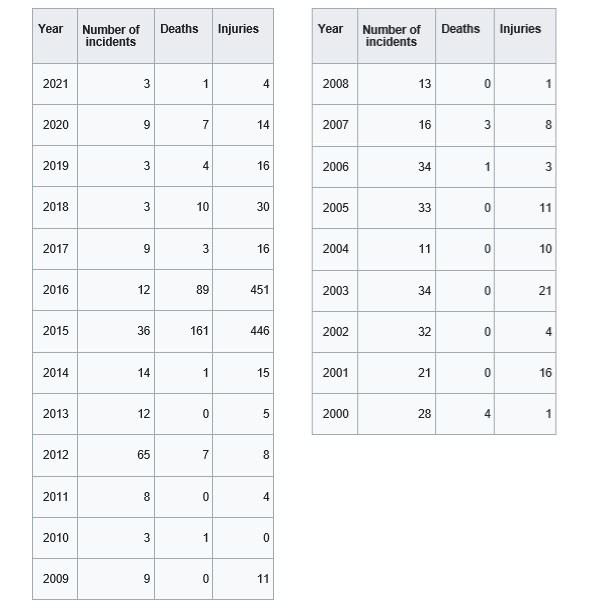
Table 1 Analysis of terrorist attacks in France, Source (National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism. (2016). Global Terrorism Databa-se (globalterrorismdb_0616dist.xlsx Archived 2016-07-10 at the Wayback Machine). Retrieved from https://www.start.umd.edu/gtd University of Maryland)
For this article, we took terrorist attacks from 2000-2021. Analyzing Table 1, it is noticeable that France is highly vulnerable to two types of terrorist threats. One comes from traditional terrorist organizations of a local character, such as ETA or FLNC, and the other comes from Islamic terrorist organizations that operate all over the world but, unfortunately, also in France. There has been an increase in violence, victims, and casualties from 2000 to the present. What do these statistics tell us? France should implement legally defined measures to prevent the bearers of a terrorist threat. Is the French robust security system not what it should be - an efficient security system? How and in what way do French security services conduct security assessments? Do they use special security science methods? On what basis do they conduct security assessments and analyses? Do they understand security prediction models? The numbers in Table 1 reasonably lead us to conclude that something is not working in the French security system, which is not the case just in France.
Analysis of Terrorist Attacks in Germany
In Germany, as in France, there are traditional or local terrorist organizations and those with an Islamist prefix that operate worldwide and have a strong presence in Germany. Special mention should be made of the ultra-left terrorist organizations that carried out various attacks on the territory of what was then West Germany and were backed by Soviet security services, from the KGB to the notorious Stasi (Crenshaw, M. 2007). Also, in Germany, a clear diagonal of terrorist attacks is visible, ranging from the terrorism of the 1960s and terrorist attacks carried out mainly by left-wing factions led by the Red Army to modern terrorism and the terrorist threat from Islamists and jihadists who have found fertile ground in Germany. The Shiite terrorist organizations present in Germany, which are involved mainly in organized crime, should not be left out of the analysis (The Institute for Defense Studies and Analyses, 1987).
Various Turkish or pro-Turkish terrorist organizations, from the Grey Wolves to the Turkophone Uyghurs, also operate in Germany. Suppose we add Kurdish Albanian organized criminal groups and many others to the long list of various movements, terrorist organizations, and organized crime groups with ties to terrorism. In that case, the security situation in Germany is highly complicated. In Germany, if we exclude Islamist terrorist attacks, all indicators indicate that the terrorist threat in this country is exceptionally high. The German intelligence services did not take the warning seriously when an Islamist in France on July 14, 2016, using a truck as a means of carrying out a terrorist attack, deliberately drove into a pedestrian zone and killed 84 citizens, and dozens more sustained various injuries. That same year, an Islamist terrorist used a truck, this time in Germany on December 19, 2016, to drive into a Christmas market at full speed, killing 12 and seriously injuring 70 victims. However, attacks on citizens with vehicles have only continued. From Sweden, Israel to the US New Orleans track attack 2025. In other words, it can be said that the intelligence and security services and institutions did not do much to prevent these attacks using this method of execution.
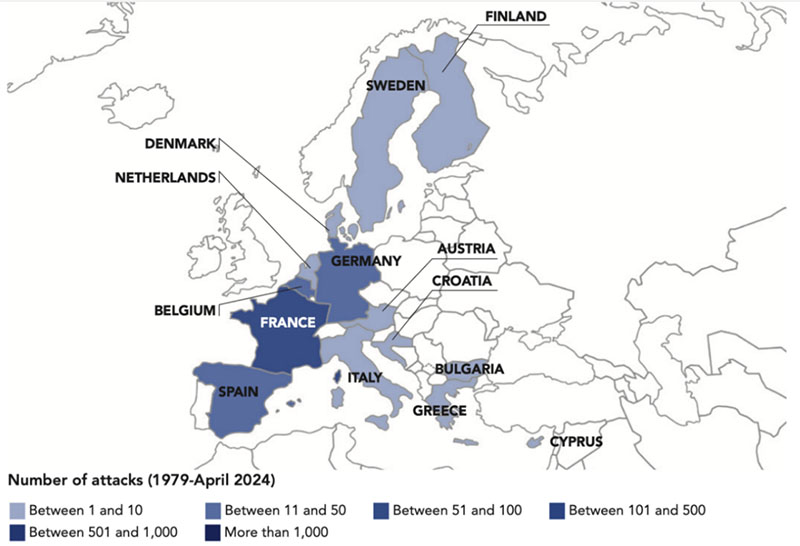
Picture 1: Islamist terrorist attacks in the World 1979-2024
Source (https://www.fondapol.org/en/study/islamist-terrorist-attacks-in-the-world-1979-2024)
Analysis of Picture 1 shows that the primary target of terrorist attacks by Islamists is Western Europe, especially Germany, France, and Spain. In addition to the key legislative assumptions without which it is impossible to respond to terrorist threats institutionally, the work of intelligence services is the most essential defense against terrorism. Statistics show that the number of terrorist attacks is increasing, which is inconsistent with the number of intelligence services against terrorist units, analysts, experts, and all others who deal with this issue. There is a discrepancy.
What is the real problem? Establishing the reasons for apparent problems requires a deeper analysis that goes beyond the scope of this article. Here, we can point to several essential elements. Based on statistics alone, experienced intelligence officer can conclude that something is not right in a given territory. Analyzing the situation is multidimensional domain through specific indicators that lead to instability, such as internal or external security risk factors. When we talk about a terrorist threat, no matter where it comes from, we can immediately agree that it is a highly complex phenomenon and requires an institutional response.
The state responds to security threats and challenges precisely through institutions. intelligence services are tasked with determining risk factors, working to prevent them, i.e., preventing them from achieving their goals, informing the top brass of the state and the legislative body to pass laws based on which state administration institutions can react and, finally, actively proposing de-radicalization measures as a fundamental element - the motivation for carrying out any terrorist attack. intelligence services and other state institutions must react to new challenges promptly and develop the New Craft of Intelligence.
The bearers of the terrorist threat are always one or more steps ahead of state institutions, so it is essential that intelligence services, first of all, also deal with predictions. If we consider Map 1, we do not understand that all regular activities that security services should undertake have actually been undertaken.
The Lone Wolf terrorist
Perhaps the example of "The Lone Wolf" can explain the inexplicable. According to the US Justice Department, "Lone Wolf" terrorism is the term used to describe someone who acts alone in a terrorist attack without the help or encouragement of a government or a terrorist organization (Hamm, M. 2013). This definition of this phenomenon does not correspond to the knowledge of professionals for several reasons. Obviously, unable to respond to this phenomenon or due to the lack of knowledge in the field of security science, some analysts, experts, and even state institutions give a completely wrong picture of this phenomenon.
According to the incorrect definition, a Lone Wolf has just radicalized himself. Here is why all this is applicable. Two elements must be present for any attack to be carried out, as we have already underlined. The first is the operational possibility of carrying out an attack, which implies the availability of weapons, explosives, or other means of execution. The second, perhaps the most important, are the motive and a trigger for carrying out the attack. In this case, the "Lone Wolf" operational possibilities are a widely spread network of Islamists and the work of several committees of the Islamic State. Above all, the media, religious, and military committees.
These committees are tasked with radicalizing those sympathizers they could not physically reach. The next important thing is the motive. Sunni Islamist organizations are organized in such a way that their main goal is to promote the establishment of a Global Islamic State or Ummah. They want to achieve this goal through the form of political Islam. To achieve political Islam, they use various methods, which in many cases also include terrorism. From these two segments alone, it is clear that the "Lone Wolf" represents a combination of ignorance and misunderstanding of this phenomenon. To prevent the " Lone Wolf operations," it is necessary to understand the phenomenon and use state institutions to prevent operational capabilities and motivations. It may seem simple when explained, but in practice, it is not. State institutions require years of experience, knowledge, and the application of the most modern technical and technological achievements to promptly suppress all internal and external security threats and ensure citizens' everyday lives and the state's functioning, including development.
In other words, "Lone Wolf" is a widely spread project of Islamists aimed at individuals whom they cannot directly and physically approach. The motivation for these terrorists comes through social networks and platforms that are set up for this purpose on those networks. The Islamic State's "Dabiq" newspaper is an ideal example. Likewise, numerous instructions on how to carry out a terrorist attack with examples of successfully carried out actions are publicly available. It is also necessary to understand the fact that from Al Qaeda to Daesh, all these organizations are horizontally structured and that leadership is actually made up of ideology where one person is easily replaced by another. So there is no "Lone Wolf". It is a well-planned network with well-planned roles of individuals within the network.
Conclusion
As mentioned, intelligence services play a key role in collecting, detecting, processing, analyzing, and predicting all data related to security risk factors, whether those coming from the internal arena or those threatening security from the outside. It is crucial to emphasize predictive analysis as a key component not only of counterterrorism but also as a key variable for all other risk factors that can threaten a country. With such an approach, which is called the New Craft of Intelligence, an important place is also occupied by applying sophisticated technology from AI to all other technical and technological responses that can aid in achieving the key missions and tasks that intelligence services face. By analyzing terrorist attacks and applying them, it is possible to reveal patterns and behaviors associated with those that pose terrorist threats. These carriers could be ultra-leftist, ultra-rightist organizations, Islamist-jihadist organizations, groups, or sub-groups that carry out terrorist attacks around the world.
Literature:
1. Trifunović, D., International Criminal Law and Terrorism, National Security and Future, 1-2 (22) 2021. Preuzeto sa https://hrcak.srce.hr/clanak/382101
2. Akrap, G., Kalinić, P. (2018). Bezposadne letjelice i terorizam. National Security and the Future, 19 (1-2), 213-219. Preuzeto sa https://hrcak.srce.hr/206497
3. Kazansky, R., Trifunovic, D., Conflict Theory - One of the Theoretical Foundations of security science. The International Strategic Studies Association, 2021.
4. Piwowarski, J., Trifunovic, D. From security science to Security Culture, RIEAS, Research Institute for European and American Studies, Athens, 2023
5. Trifunović, D., Stojaković, G.,Vračar., M., Terrorism and Vehabizam, Filip Visnjic, Belgrade, 2011.
6. Todorovic, B., Trifunovic,D., Security science as a scientific discipline – technological aspects, Security Science Journal, Institute for National and International Security, Belgrade, 2020.
7. Crenshaw, M. Terrorism in Context, The Pennsylvania State University Press, University Park, PA, 2007, pp.160-210
8. News Review on West Asia, The Institute for Defense Studies and Analyses.18 Edition, Manohar Parrikar India, 1987.p.478
9. Hamm, M., Lone Wolf Terrorism in America, US Department of Justice, 2013 https://www.ojp.gov/ncjrs/virtual-library/abstracts/lone-wolf-terrorism-america
10. Aljazeera, 2024, retrieved 17.04.2025 Missile fired from Yemen lands in Israel, https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2024/9/15/missile-fired-from-yemen-lands-in-israel-setting-off-sirens-military-says
11. Serkan, B. Daesh" s Drone Strategy Technology and The Rise of Innovative Terrorism, Istanbul: SETA Publications, 2017.
Cite this article:
APA 6th Edition
Trifunović, D. (2025). Intelligence and Counterterrorism. National Security and the Future, 26 (1), 179-192. Preuzeto s https://hrcak.srce.hr/331827
MLA 8th Edition
Trifunović, Darko. "Intelligence and Counterterrorism." National Security and the Future, vol. 26, br. 1, 2025, str. 179-192. https://hrcak.srce.hr/331827. Citirano DD.MM.YYYY
Chicago 17th Edition
Trifunović, Darko. "Intelligence and Counterterrorism." National Security and the Future 26, br. 1 (2025): 179-192. https://hrcak.srce.hr/331827
Harvard
Trifunović, D. (2025). 'Intelligence and Counterterrorism', National Security and the Future, 26(1), str. 179-192. Preuzeto s: https://hrcak.srce.hr/331827 (Datum pristupa: DD.MM.YYYY)
Vancouver
Trifunović D. Intelligence and Counterterrorism. National Security and the Future [Internet]. 2025 [pristupljeno DD.MM.YYYY];26(1):179-192. Dostupno na: https://hrcak.srce.hr/331827
IEEE
D. Trifunović, "Intelligence and Counterterrorism", National Security and the Future, vol.26, br. 1, str. 179-192, 2025. [Online]. Dostupno na: https://hrcak.srce.hr/331827. [Citirano: DD.MM.YYYY]